CDN_Notes
Content Delivery Network
Below is all my personal understandings
Full Name :Content Delivery Network or Content Ddistribute Network
Basically, CDN solution solves a common issue: There will always be a bottleneck on the internet, due to different service providers, or geo locations, etc. Which impact the network performance. On the other hand, Latency control is one of the most important indicators nowadays. With CDN, You can deliver a more reliable and stable network by putting certain Servers in certain places in the internet, and building a intelligent network on top of the internet. CND can redirect customer reuquests to the fastest server(maybe not the closest), based on network throughput, response time, latency, loadbalancing status, physical distance(main factor that impact latency).
Based on above description, here comes the objective of the CDN solution:
To solve the latency problem due to bandwidth, server performance, geo location limitations. Use case includes but not limited to: website acceleration, play on request, live video/voice steaming, etc. Which can improve user experience and success rate, and avoid network congestion.
Pros:
Let’s say you are running a website, There will be some key indicators to make you success:
- Attractive content
- Fast access
- Support frequent user interactions
- Can browse anywhere without restrictions
Elaboration of item 4: you must consider global users experience, which will introduce a very complex network environment, such as: Network security policies/laws in different countries, physical distance, Datacenter maintenance, ISP availability, etc. In addition, when your business grows bigger, your website for sure will add more features and contents, like images, vidtos, CSS, APIs, etc. Plus more user requests and for sure some DDoS attacks. All these factors might slow you down and impact user experience.
Every single second of delay on your website response, you will lose your users and some users may never come back again.
Which Introduct one of the key benefits of CDN:
- Accelerate your response time.
It also have some other benefits, such as: 2. Full converage of the Internet, eliminate ISP/geolocation limitation. 3. Secure your Website - CDN use loadbalance and distributed storage, which also improves website reliability. - If one of the CDN node goes down, other node will takeover, so theoretically your website will never go down. 4. Reduce Operation complexity. - Servers are synced between each other, One time setup and let automation run in background. No need to put too much effort on individual servers. - If you choose CDN providers, then almost ZERO effort on maintaining the CDN network/service, CDN providers will take care of that. You can focus on your core business.
Basic CDN infrastructure:
- When user requests URL, local DNS will forward requests to CDN DNS server.
- CDN DNS server return CND Global Load Balancer IP back to user.
- User send HTTP/HTTPS request to Global Load Balancer.
- Based on user IP address and content user request, choose one of the fastest/closest Local Load Balancer, and local load balancer will choose one cache server(or cluster) to respond.
- Criteria include and may not limit to: user IP, Content of URL, Server performance, latency.
- User get response from cache server, if the cache server doesn’t have the requested resource, it will request content from upper layer caching server, until the source server, and pull resource to local.
CDN Component
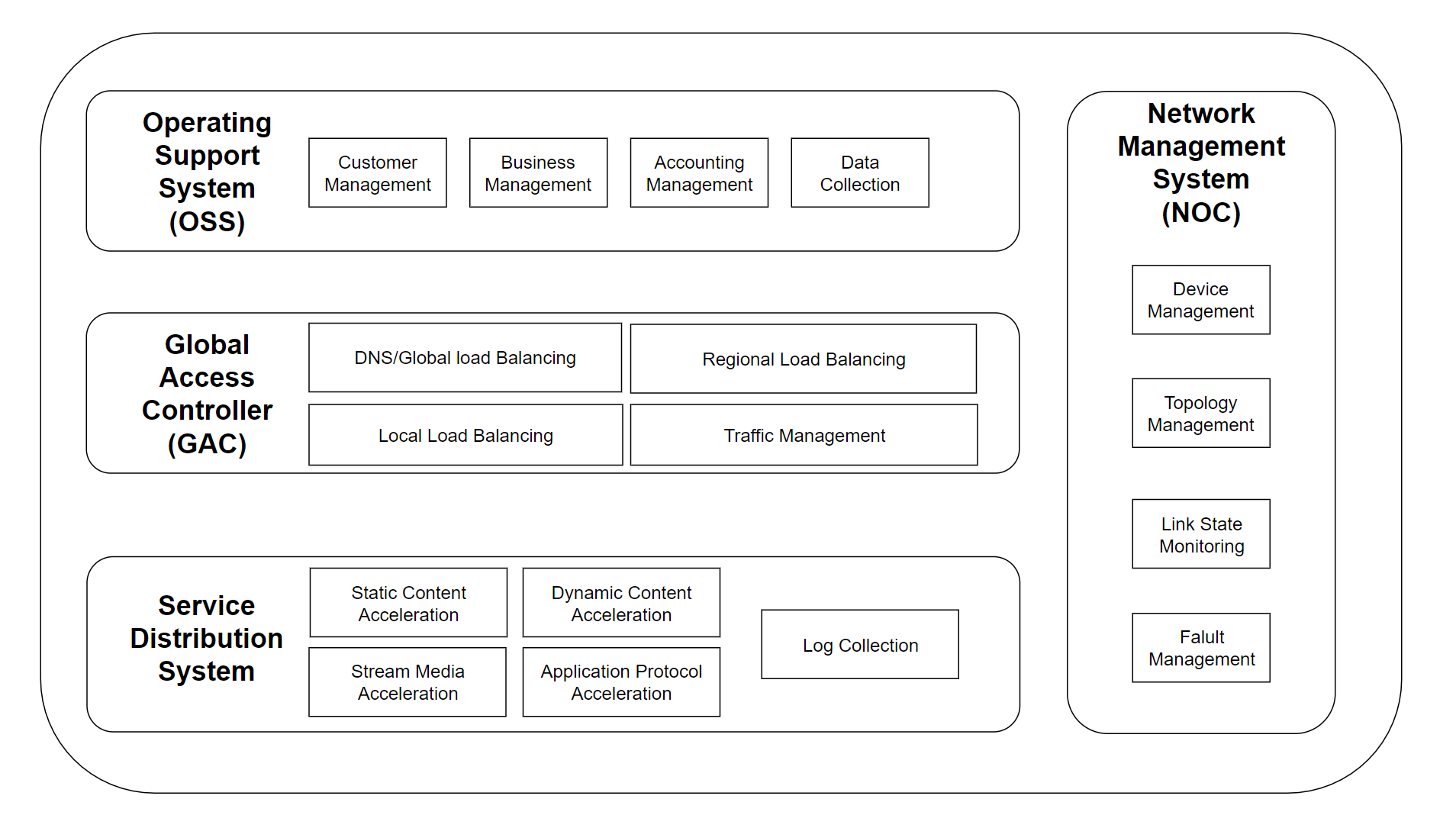
CDN logic workflow
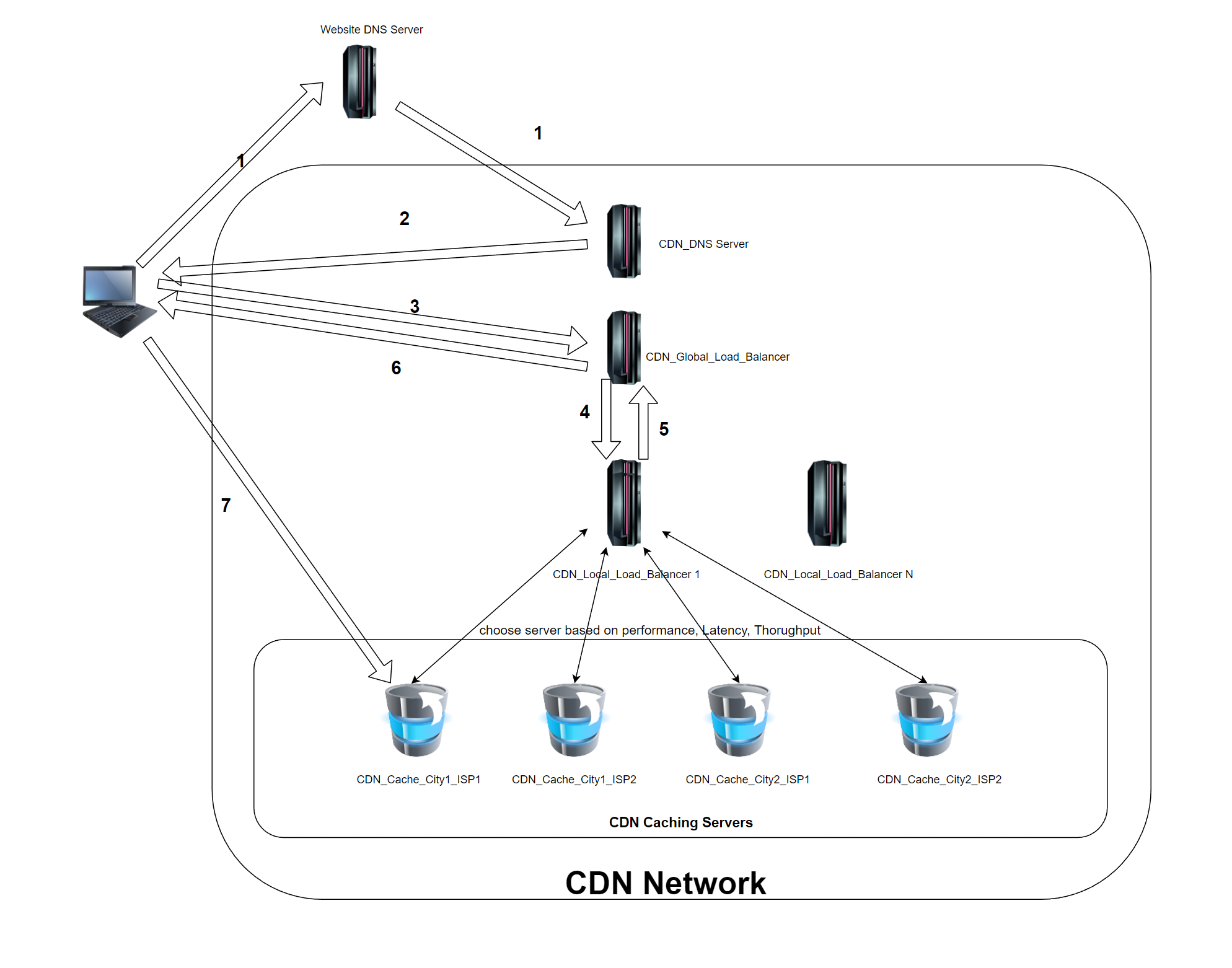
GLSB logic workflow
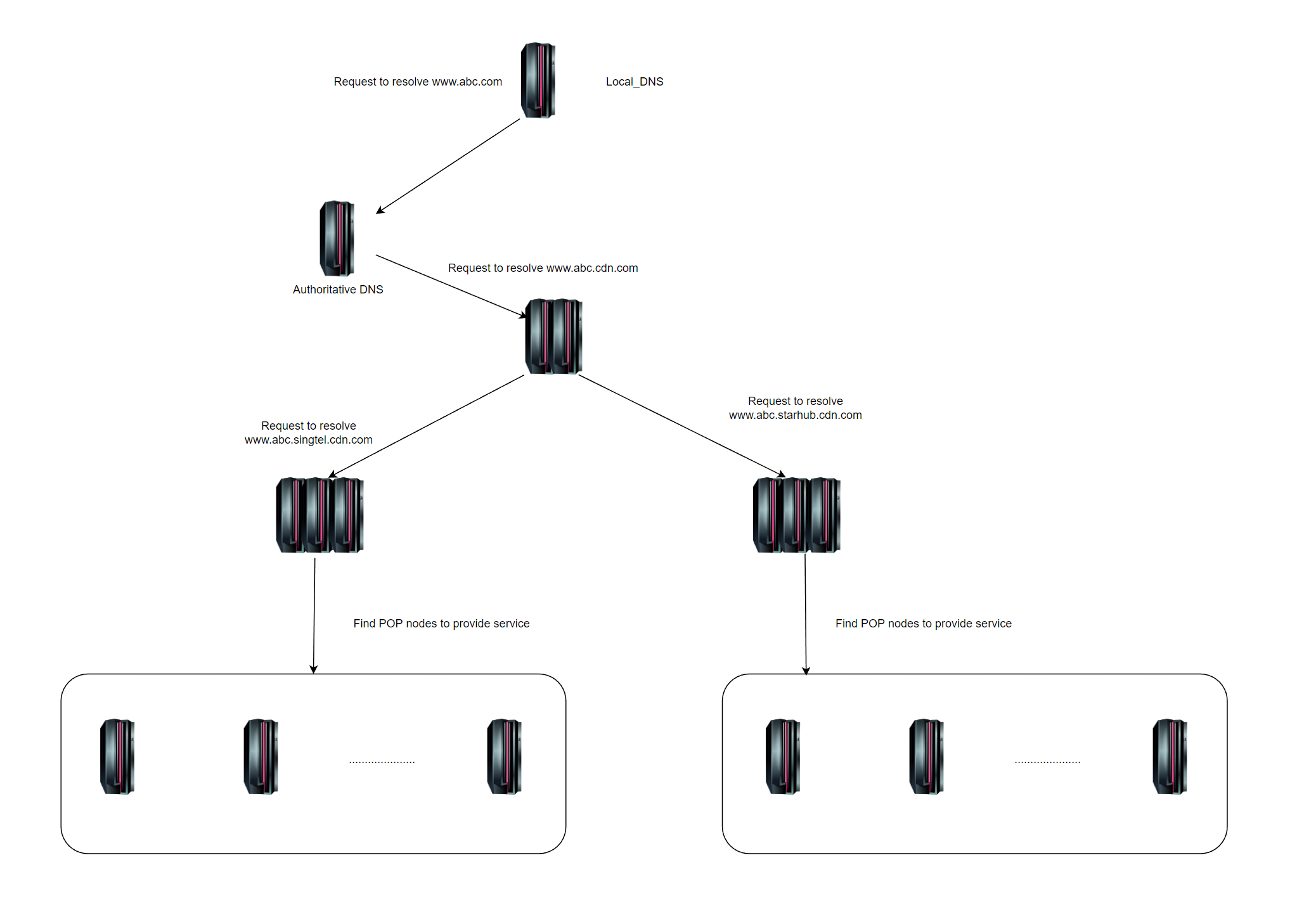
Summary:
CDN is a policy based service as a whole, Which include [Distributed Storage], [Traffic Management], [Content management] three key elements.
[Traffic Management] & [Content Management] is the core of CDN.
Example:
You are using Singtel and your home broadband service provider, if you access a certain website in StarHub, then you may experience latency issue. However, if the Website use CDN, and have caching server in Singtel, you will get response from caching server in singtel directly, the caching server will either cache your requested content or query original server for you in a faster speed. So you won’t have any latency issue. And if the original server goes down, caching server will also provide partial or full service based on what you request, which is better than you can’t access at all.
Common misunderstandings on CDN:
- CDN accelerates Server or Domain Name?
- Accelerate Domain name.
- What’s the difference between CDN and mirrored website?
- CDN is transparent to users, it helps user to choose the fastest one. more user-friendly. On the other hand, mirrored website normally provides a list of mirrored URLs, and user may not be able to know which one is the fastest one.
- CDN has health checks on its nodes, if it finds a certain node is unhealthy, it will remove it from the list. mirrored website can’t do this.
- Easy to deploy, no need to do any modifications on the original server.
- What if I put 1 server in Singtel and one server in Starhub in above case? Dose it make any difference with CDN?
- It makes you a smaller version of CDN, but sync, maintenance, etc need to be done by yourself
- Two servers are both original servers, and data integrity maybe a issue. (I update A on singtel server, then use cell phone in Starhub to access and mofify my record to B at the same time, which one is the real&Authenticate one? take latency into consideration)
- If it’s a big country, let’s say China, you put one server in HK, and user is in BeiJing, physical distance also increase latency. CDN caching can make you have caching server in each city and if you choose CDN provider, you don’t need to rent a server room/rack in each city. Which increase user experience and reduce operation cost.
- Do I need to modify my original server if adopte CDN service?
- normally no need. Only you got some services to detect customer geographic location/IP address.
- How caching server knows a update from the original server?
- There is a URL push/synchronization option in CDN management console. When there is a update, can trigger this URL push and it will push new content to all caching servers and delete old one in caching server.
- If I add new content in original server, do I need to do a URL push?
- No need. Because it’s not in caching server. Caching server will pull on user request.
- What if I got some sub pages, contents that is time sensitive? Keep doing URL push?
- Use dynamic web, asp, php, jsp, or other dynamic web won’t be cached by CDN. Or put your time sensitive contents in a different Domain name and don’t use CDN, CDN web refer to this URL.
- Which scenario we can’t use CDN or CDN is not a suitable solution?
- Very limited users, or only serve certain/designated user groups.
- Very localized users, like “River Vally Tennis Club”
- Complex regulations, like user data is sensitive.
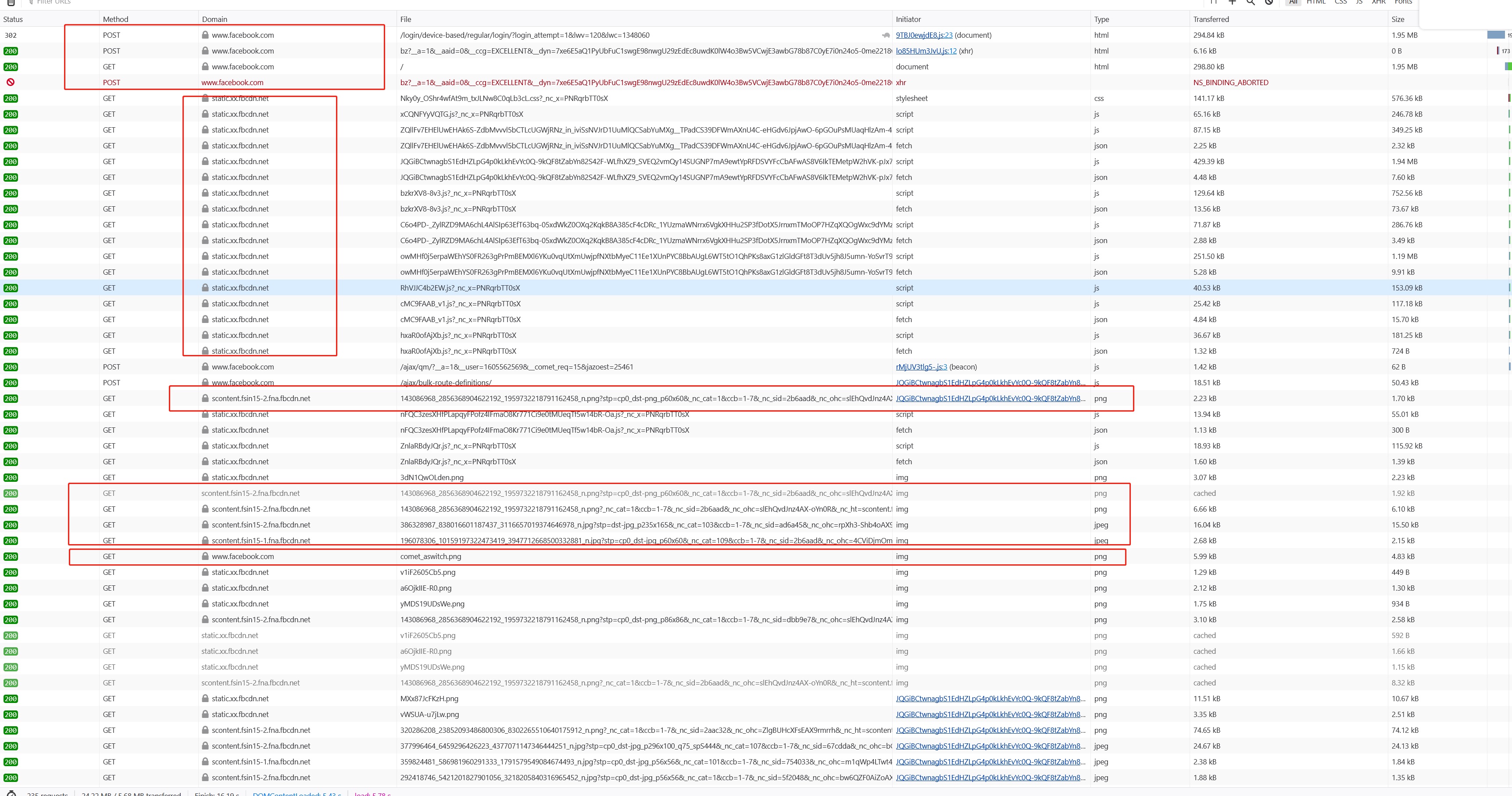
Let’s use facebook as example: When I Open Facebook URL, in F12 in firefox it’s shown as below:
Some DNS related commands
skou@my_macbook% dig @8.8.8.8 google.com
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> @8.8.8.8 google.com
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 61025
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 6, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;google.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
google.com. 192 IN A 142.251.12.138
google.com. 192 IN A 142.251.12.101
google.com. 192 IN A 142.251.12.139
google.com. 192 IN A 142.251.12.113
google.com. 192 IN A 142.251.12.100
google.com. 192 IN A 142.251.12.102
;; Query time: 10 msec
;; SERVER: 8.8.8.8#53(8.8.8.8)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 12 15:45:13 +08 2023
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 135
skou@my_macbook% dig www.google.com
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> www.google.com
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 59567
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 6, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.google.com. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.google.com. 70 IN A 142.251.10.103
www.google.com. 70 IN A 142.251.10.99
www.google.com. 70 IN A 142.251.10.104
www.google.com. 70 IN A 142.251.10.105
www.google.com. 70 IN A 142.251.10.147
www.google.com. 70 IN A 142.251.10.106
;; Query time: 25 msec
;; SERVER: 100.64.0.1#53(100.64.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 12 15:42:20 +08 2023
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 139
The system will list all google.com DNS records that it finds, along with the IP addresses.
skou@my_macbook% dig google.com ANY
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> google.com ANY
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 21051
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 14, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;google.com. IN ANY
;; ANSWER SECTION:
google.com. 265 IN A 142.251.12.139
google.com. 265 IN A 142.251.12.100
google.com. 265 IN A 142.251.12.101
google.com. 265 IN A 142.251.12.113
google.com. 265 IN A 142.251.12.102
google.com. 265 IN A 142.251.12.138
google.com. 294 IN AAAA 2404:6800:4003:c11::8b
google.com. 294 IN AAAA 2404:6800:4003:c11::64
google.com. 294 IN AAAA 2404:6800:4003:c11::66
google.com. 294 IN AAAA 2404:6800:4003:c11::8a
google.com. 26737 IN NS ns4.google.com.
google.com. 26737 IN NS ns1.google.com.
google.com. 26737 IN NS ns3.google.com.
google.com. 26737 IN NS ns2.google.com.
;; Query time: 116 msec
;; SERVER: 100.64.0.1#53(100.64.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 12 15:48:30 +08 2023
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 319
skou@my_macbook% dig google.com +noall +answer
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> google.com +noall +answer
;; global options: +cmd
google.com. 214 IN A 142.251.12.113
google.com. 214 IN A 142.251.12.102
google.com. 214 IN A 142.251.12.138
google.com. 214 IN A 142.251.12.139
google.com. 214 IN A 142.251.12.100
google.com. 214 IN A 142.251.12.101
dig google.com +trace
The +trace option lists each different server the query goes through to its final destination. Use this command option to identify the IP address where traffic is dropping.
skou@my_macbook% dig -x 157.240.15.35
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> -x 157.240.15.35
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 15141
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;35.15.240.157.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR
;; ANSWER SECTION:
35.15.240.157.in-addr.arpa. 2304 IN PTR edge-star-mini-shv-03-sin6.facebook.com.
;; Query time: 23 msec
;; SERVER: 100.64.0.1#53(100.64.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 12 15:51:44 +08 2023
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 108
skou@my_macbook% dig www.facebook.com ANY
; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> www.facebook.com ANY
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 33350
;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.facebook.com. IN ANY
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.facebook.com. 95 IN CNAME star-mini.c10r.facebook.com.
;; Query time: 30 msec
;; SERVER: 100.64.0.1#53(100.64.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Jul 12 15:53:43 +08 2023
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 74