Low_Latency_Network_Architecture
exchange trading system
General Description of Exchange trading system architecture
Business flow:
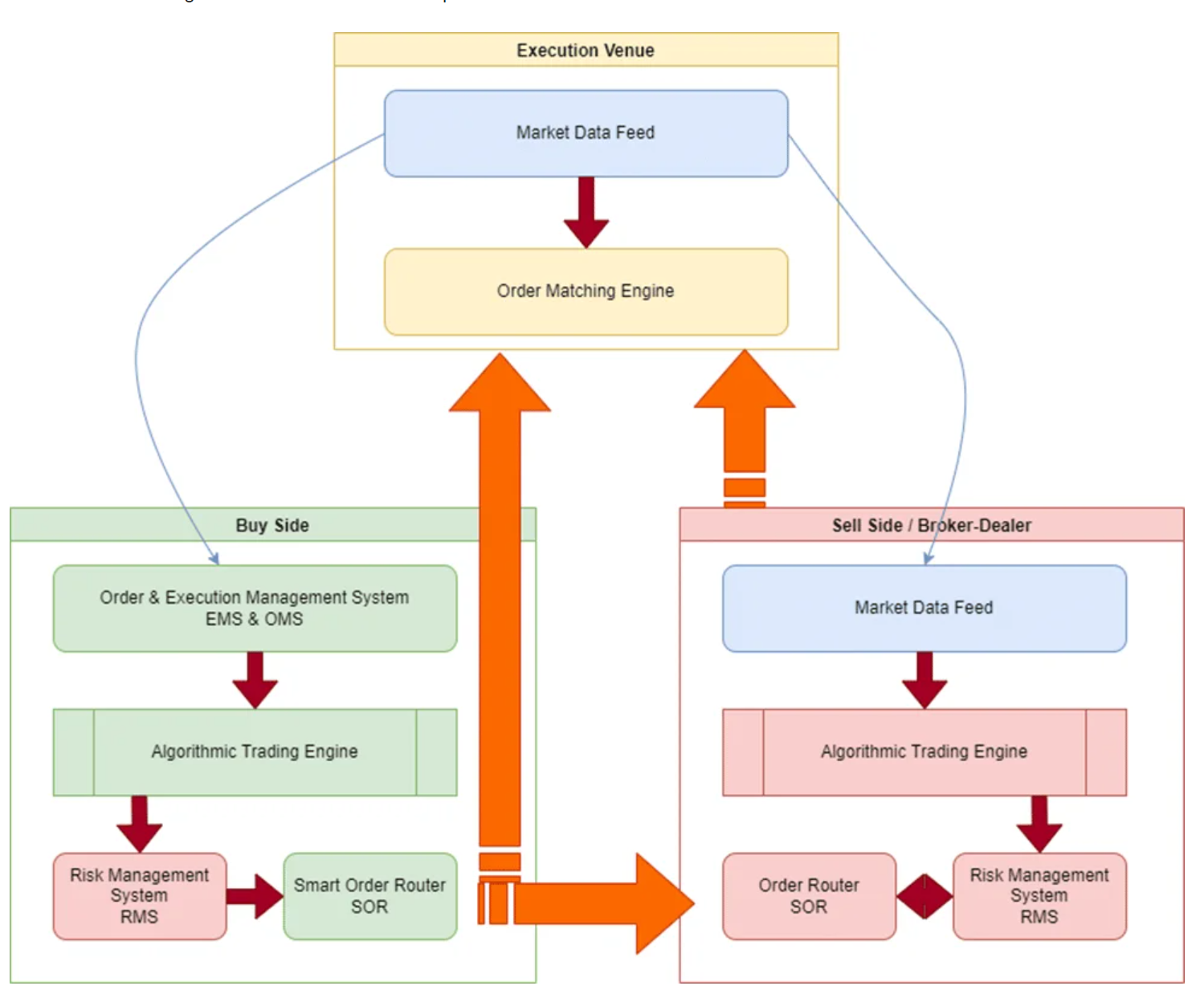
Below is a very simple example of all the key components of a exchange trading system. Legacy system commonly run o a centralized server to process multiple tasks, and network is holding marketdata, order routing system, Clearing.
The lower latency the trading system is, the higher amount of orders it can handle. To me, in terms of the HFT firms, the most important thing is the lower the latency is, the higher chance you get the information and make the deal, which can make you a better advantage vs other trading firms.
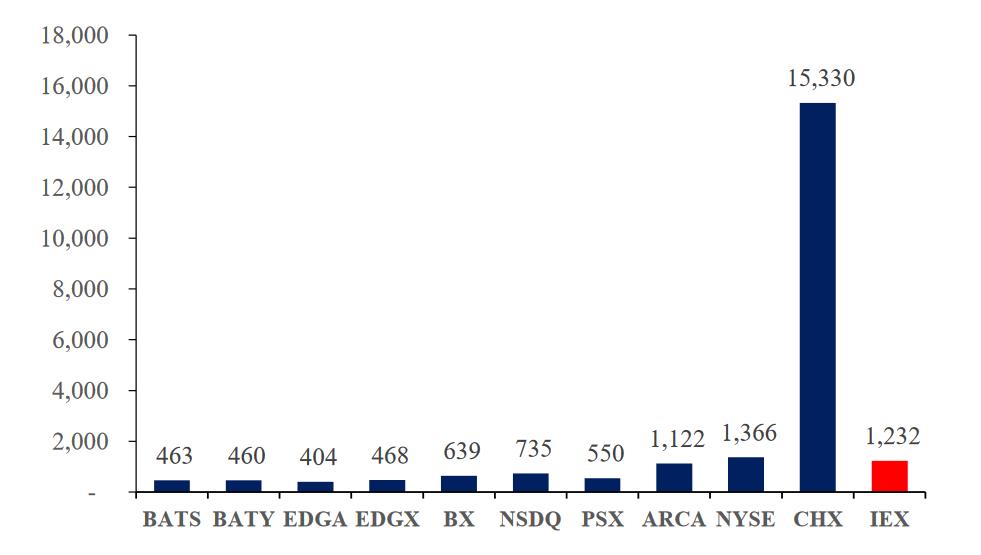
Time Measured in microseconds
HFT latency data is confidential can’t find, use above for reference only
The commonly used technics to reduce latecncy is :
Distributed matching engine system
Independent Messaging Bus
Low Latency Network
Trading firms system optimization
Distributed matching engine/system
Normally the way to use distributed system is to put different types of product (or subset of products) into different server to do the matching. This is also called multi matching engine.
However, Distributed matching engine/system bring another issue: Time Consistency.
Traditional way is to use NTP to synchronize clock. But this approach doesn’t meet the requirement for trading. Thus PTP protocol is introduced.
System can use either inband or out of band PTP to synchronize clock. PTP source normally get from GPS clock.
If use inband, congestion and micro burst might bring some troubles to PTP. Although PTP has its own label in header to timestamp the latency. The best way is to use out of band PTP.
For trading front system, normally need to make some label in packet header for the packet arrival time, which can mark the request submition time precisely, and queue it in the right sequence in matching engine.
Normally use L1 FanOut switch that is based on FPGA for out of band dedicated PTP network. Although it will occupy additional NIC port on server, it’s worth to do it. NIC normally use SMA interface and OXCO to keep server time precision.
Independent Message Bus Interface
In terms of business model, matching engine acts as a center for market data, Ordering & listing, and Clearing. It would bring some congestions, performance or other potential risks if use these 3 business in the same network.
So it’s the best to use separate network to handle different types of traffic.
Benefit of this is:
- NIC can hardcode to accelerate certain messages
- Micro burst can be isolated
- Predictable traffic patterns
- Less complexity for operation
Traffic Pattern:
- Listing and distributed matching, order distribution, it’s a standard many to many traffic, Normally use low latency ASIC switch based on MAC address. Such as cisco Nexus 3548 or Arista 7150.
- Clearing and market data summarization is standard many to one traffic, normally no need MAC address lookup, can forward packet to designated port. So can use FPGA with MAC IPCORE switch, such as Cisco FusionMux and Arista MetaMux switches.
- Market data is standard one to many communication, can use L1 switch to duplicate packet to multiple ports, no need to use multicast OIF querying mechanism.
Note: There used to use modular switch or router&multicast to do market data distribution, but due to different mechanism to duplicate multicast packet, there is a possibility unequal latency. But use L1 switch Fan Out can guarantee absolute fairness.
Low Latency Network
Microburst:
In trading network, there is a very common and obvious pattern which is microburst, if we see traffic in a longer timeslot, traffic per second is very minimal, but if we zoom in to milliseconds, sometimes traffic will hit the maximum.
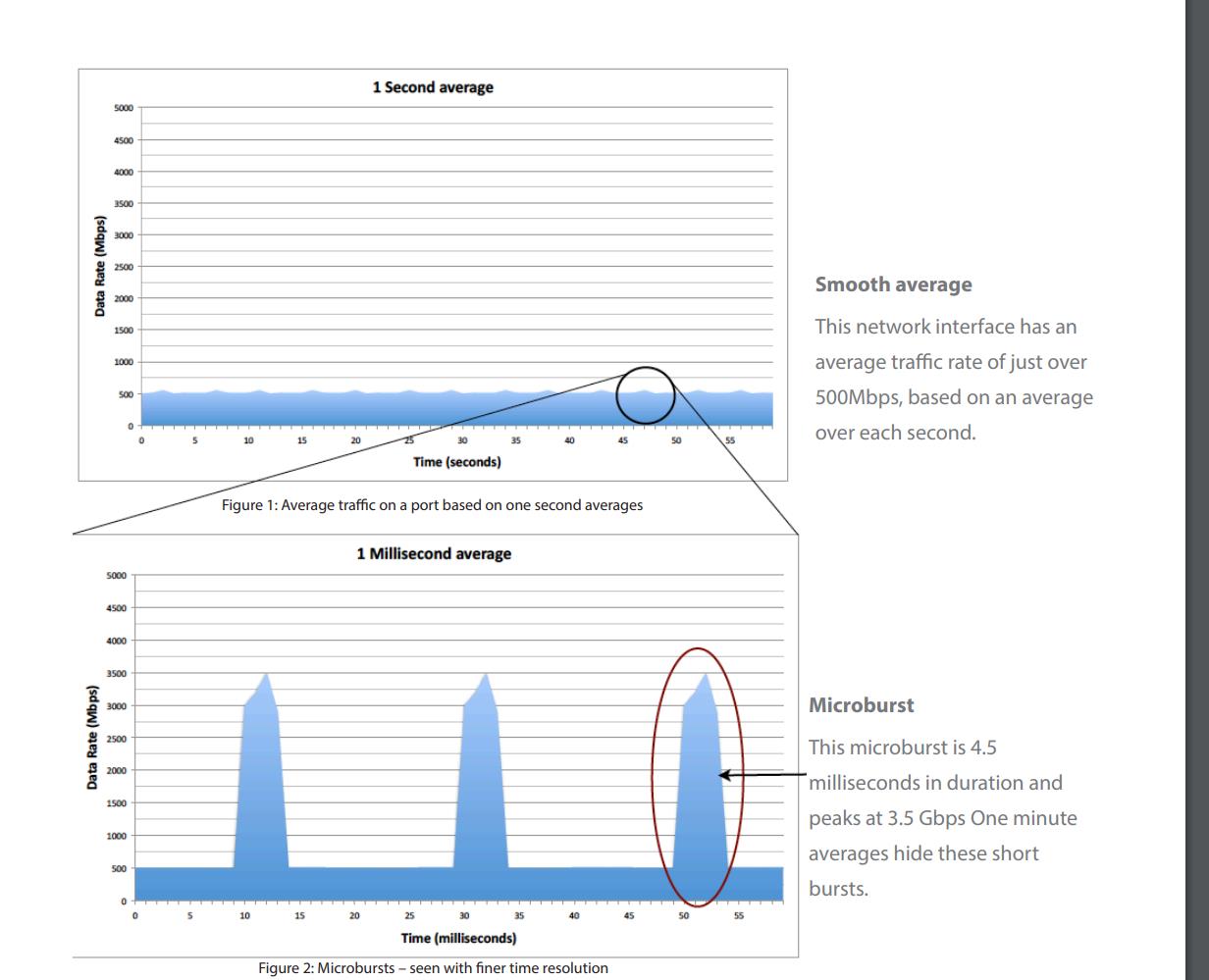
From Arista official white paper
Use low latency switch or increase bandwidth can reduce the latency caused by microburst, but higher bandwidth also increases encoding/decoding delay. Packet number is very minimal in microburst, but higher bandwidth use FEC encoding can increase latency. So best solution is to use 10G fiber or 25G fiber with RS-FEC disabled. (eg: some cisco switch can support RS-FEC disabled with high quality fiber within 30 meters). For to further reduce latency, can use Passive Twinax Direct Attached Cable.
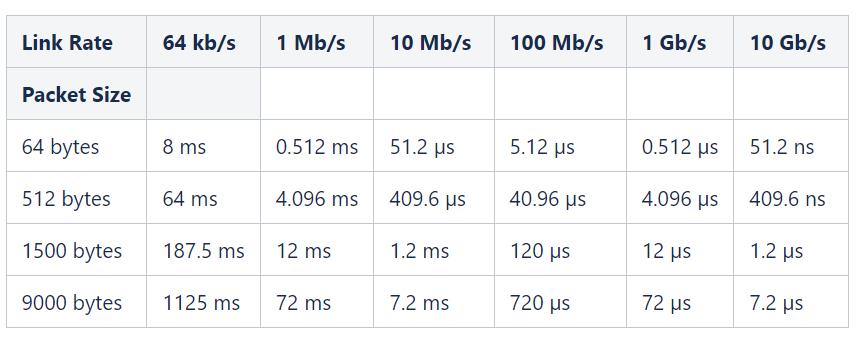
From Wiki
Another optimization is on system side, most of the trading applications are based on TCP (reliable). But traditional linux core doesn’t do too much optimization on the latency, and many to one TCP incast also increase latency.
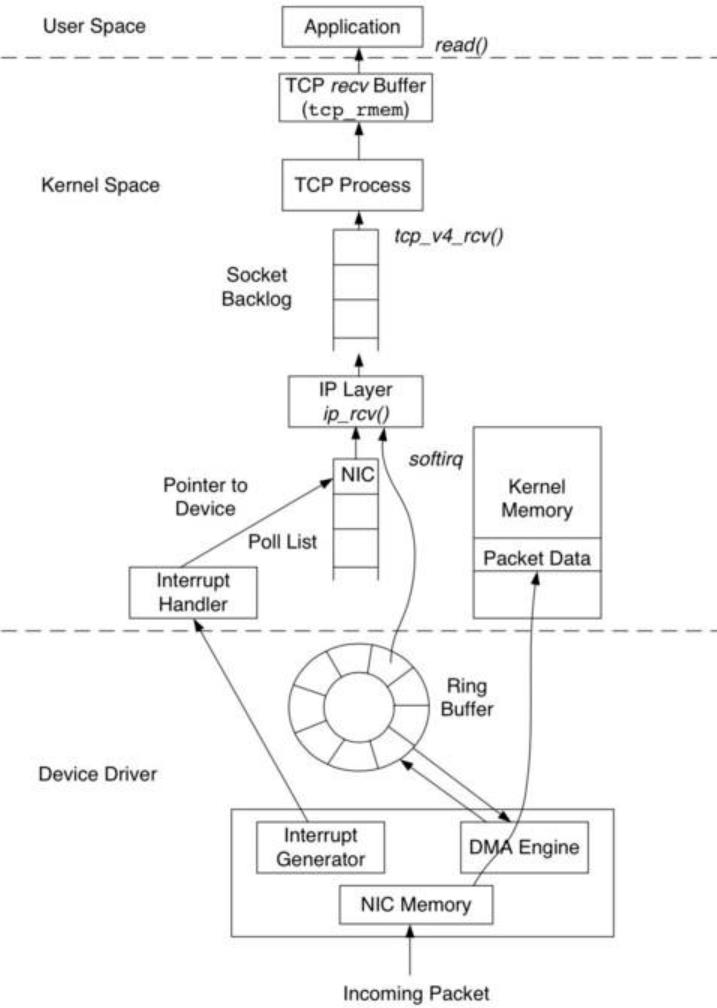
Common Solution:
- Use InfiniBand network to restructure the communication, but due to the potential risk of I&R, and cost, etc, very limited firms use this.
- ROCE(RDMAover Converged Ethernet): Also used by other industries that have requirements on low latency, (AI/Storage, etc), such as Nvidia, it aquires Mellanox for this. But there is limited adoption on Trading industry because it requires huge modifications on TCP coding.
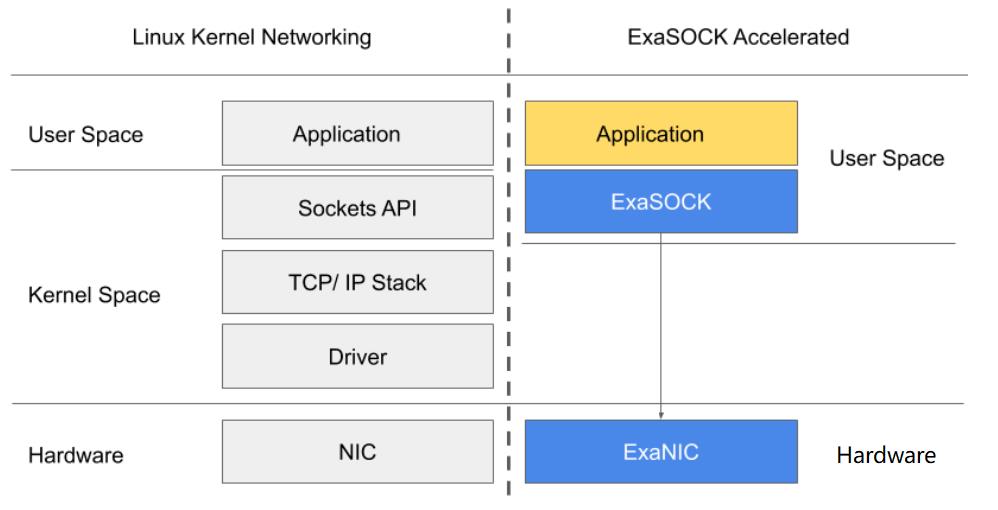
- Kernel Bypass, Commonly used in Trading industry, achieved by use certain NIC and driver. Applications or system side modifications is minimal, such Onload (Solarflare) and ExaSOCK (Exablaze).
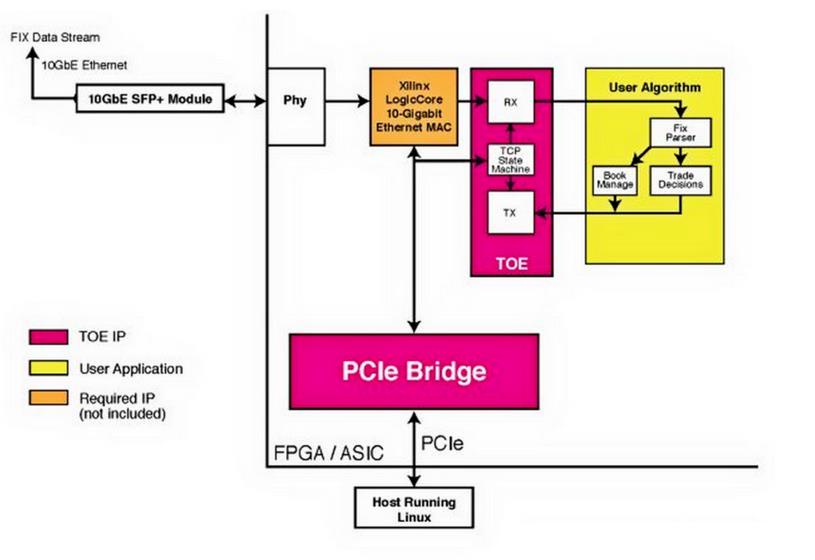
- TCP Offload, Build TCP logic on FPGA, so it process data independent of system. Trading firm can prioritize the sequence by price or time. And once find a match condition, forward to maching engine.
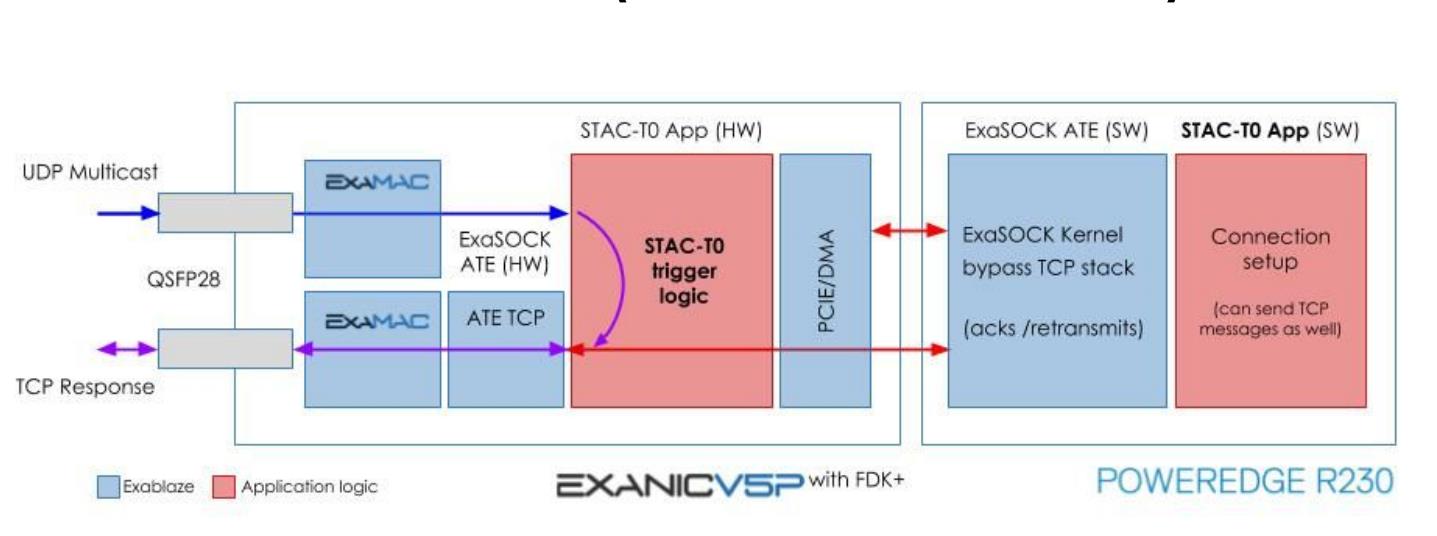
- Hybird mode, mixture of TCP Offload Engine and TCP Kernalbypass, like Exablaze FDK-XP.
- Besides this, on system side optimization is focused on CacheLine, BIOS, use high frequency CPU or CPU core binding, or CXL, etc.